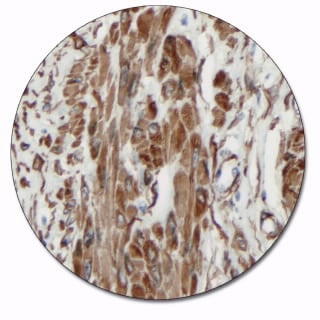
Actin (Smooth Muscle)
This antibody labels smooth muscle cells, myofibroblasts and myoepithelial cells. It is a useful aid for classification of leiomyomas, leiomyosarcomas, and pleomorphic adenomas.
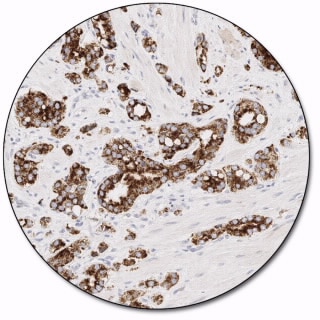
AMACR
Recognizes a 382-amino-acid protein, alpha-methylacyl-CoA racemase (AMACR), that was identified by cDNA library subtraction in conjunction with high throughput microarray screening of prostate adenocarcinomas. AMACR, also known as P504S, is an enzyme that is involved in bile acid biosynthesis and β-oxidation of branched-chain fatty acids. Results aid in the classification of premalignant high-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia (HGPIN) and prostate adenocarcinoma. AMACR is present at low or undetectable levels in glandular epithelial cells of normal and benign hyperplastic prostates.
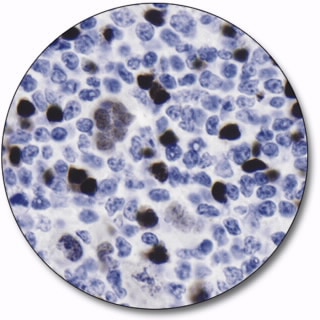
B-Cell-Specific Activator Protein
B-cell-specific activator protein, BSAP, also known as Pax-5, is a transcription factor expressed in B cells. Antibodies to BSAP may be useful for the identification of pro, pre, and mature B cells and for classification of lymphomas and subclassification of classic Hodgkin’s lymphoma and anaplastic large cell lymphoma of the T and null-cell type.
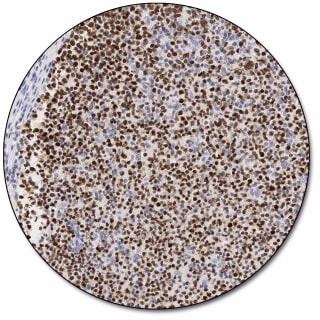
BCL6 Protein
The BCL6 gene encodes a 706 amino acid nuclear protein of the Kruppel-type zinc finger protein. It is rearranged in about 30% of diffuse large B-cell lymphomas, and is expressed predominantly in normal germinal centre B cells and related lymphomas . The antibody is a useful aid for classification of follicular lymphomas, diffuse large B-cell lymphomas, Burkitt’s lymphomas, and nodular, lymphocyte-predominance Hodgkin’s lymphoma. The BCL6 antibody, together with BCL2 antibody, is also a useful aid in classification of mantle cell lymphomas, and nodular, lymphocyte-predominance Hodgkin’s lymphoma. BCL6 protein is not expressed in B-CLL, hairy cell leukemia, mantle cell and marginal-zone derived lymphomas.
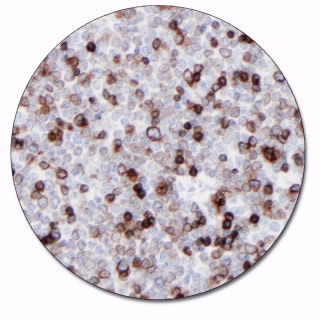
CD3
Synthetic peptide from the intracellular part of the e-chain of human CD3 was coupled to bovine thyroglobulin and used for immunization. The antibody is a pan-T cell marker for identification of T cells. It is well-suited for labeling reactive T cells in tissue with lymphoid infiltrates, and for classification of T-cell neoplasms. The antibody shows a stronger labeling intensity than corresponding monoclonal antibodies to CD3, and should, generally, be preferred on formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue sections.
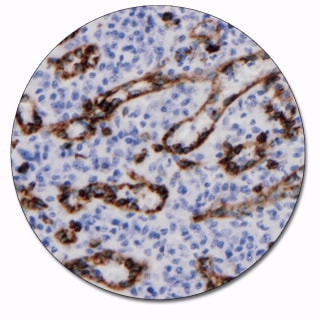
CD8
CD8 is a 68 kDa transmembrane glycoprotein expressed as a heterodimer by a majority of thymocytes, and by class I major histocompatibility complex restricted, mature, suppressor/cytotoxic T cells. The antibody is a useful aid for classification of cytotoxic/suppressor T-cell lymphomas.

CD20
CD20 is a transmembrane, non-glycosylated protein expressed on B-cell precursors and mature B cells, but is lost following differentiation into plasma cells. In resting B cells, CD20 appears in a 33 kDa non-phosphorylated form. After mitogen stimulation, CD20 becomes heavily phosphorylated (35-37 kDa isoforms), and it is a dominant phosphoprotein in activated B cells. The antibody reacts with an intracytoplasmic epitope localized on the CD20 antigen and labels cells of the B-cell lineage. It is a useful aid for classification of neoplasms of B-cell derivation.

CD45, LCA
CD45 is a transmembrane glycoprotein expressed on most nucleated cells of hematopoetic origin. On human leucocytes, five different isoforms of CD45 have been identified, named ABC, AB, BC, B and 0. Clone 2B11 reacts with all known isotypes of the CD45 family and clone PD7/26 has been clustered as anti-CD45RB. The antibody is a useful aid for classification of lymphoid neoplasms.

CD117, c-kit
The antibody labels the transmembrane tyrosine kinase receptor CD117/c-kit, located in hematopoietic stem cells, melanocytes, mast cells, Cajal cells, germ cells, basal cells of skin, and mammary ductal epithelia. Antibodies to CD117 may be useful for the classification of several cancers expressing c-kit, including gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs), mast cell diseases, acute myeloid leukemia (AML), small cell lung carcinoma (SCLC), and Ewing’s sarcoma.
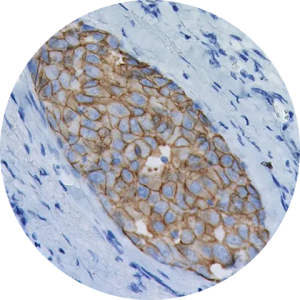
c-erbB-2 Oncoprotein
A synthetic peptide, coupled to keyhole limpet hemocyanin, has been used for immunization. The peptide represents part of the predicted 185 kDa oncoprotein encoded by ERBB2, also termed HER2 or NEU. The antibody recognizes an epitope on the cytoplasmic part of the cell membrane-bound c-erbB-2 oncoprotein. Overexpression of c-erbB-2 oncoprotein has been found in 25-30% of human breast carcinomas.
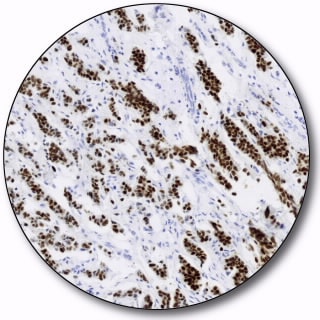
Estrogen Receptor α
This monoclonal rabbit antibody reacts with human estrogen receptor α (ER α). Estrogens have been found to be preferentially concentrated in the estrogen target organs of animals and in human breast cancers, and it is well documented that the mitogenic effects of estrogen are mediated by ER. Historical studies have shown that ER status is correlated with untreated outcome and with response to anti-hormonal therapy, e.g. tamoxifen. The antibody can used in the semi-quantitative detection of human estrogen receptor in tissue sections of human breast cancer by immunohistochemistry for assessment of estrogen receptor status in human breast carcinomas.
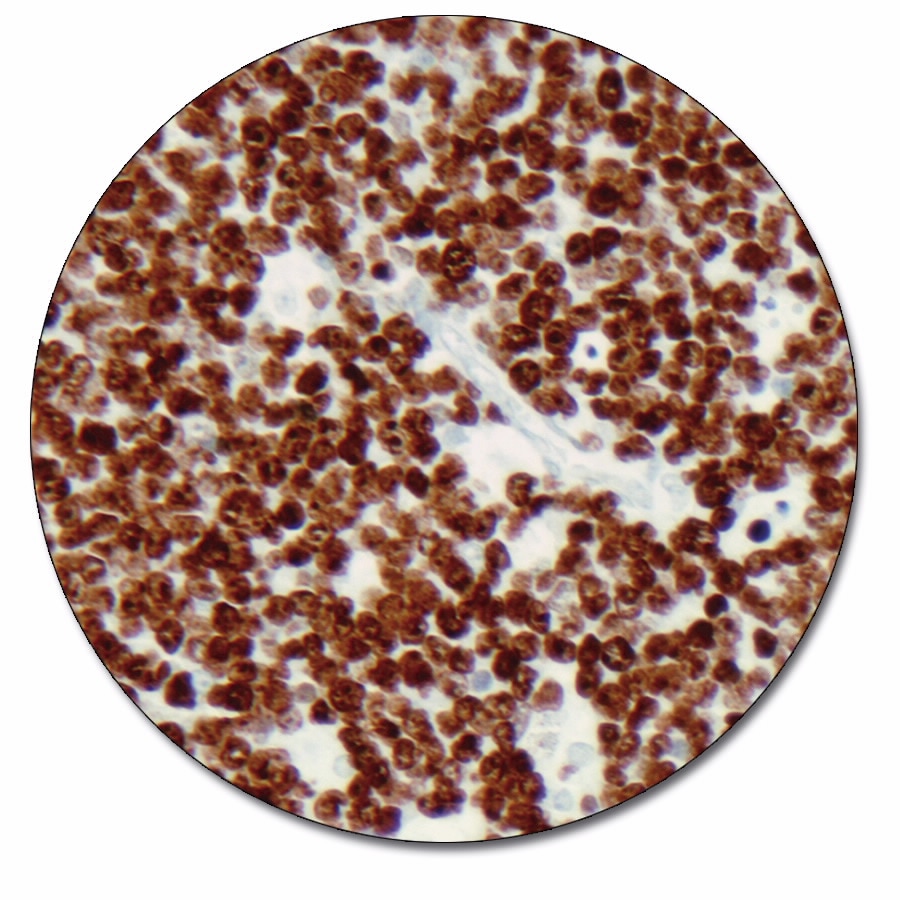
Ki-67 Antigen
With more than 4000 literature citations, the MIB-1 antibody has now been established as an important monoclonal mouse antibody for the demonstration of the Ki-67 antigen in formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded specimens. The Ki-67 antigen is a large nuclear protein (345, 395 kDa) preferentially expressed during all active phases of the cell cycle (G1, S, G2 and M-phases), but absent in resting cells (G0-phase). The antibody is a useful aid for classification of a variety of tumors.
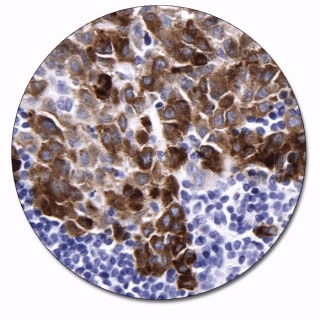
Melan-A
Melan-A, isolated as a melanoma-specific antigen, is a transmembrane protein, which is expressed in skin, retina and the majority of cultured melanocytes as well as in melanomas and angiomyolipomas. The antibody is a useful aid for classification of melanomas and adrenocortical carcinomas. The antibody is also a useful aid for classification of angiomyolipomas.

MLH 1
Mismatch repair gene hMLH1 is a ubiquitous gene encoding the mismatch repair protein (MMR) known as MutL protein homolog 1 (MLH1). MLH1 is utilized by normal proliferating cells to repair point mutations that may occur during DNA replication. Antibodies to MLH1 are a useful aid for classification of colorectal cancer.
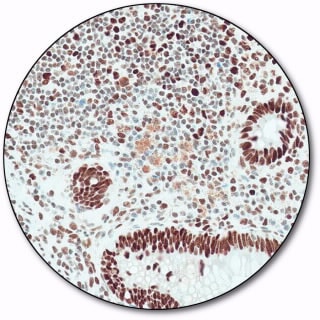
MSH 2
MutS protein homolog 2 (MSH2) is part of the mismatch repair (MMR) pathway which is utilized by normal proliferating cells to repair mutations that may occur during DNA replication. Antibodies to MSH2 are a useful aid for classification of tumors of the gastrointestinal tract, including associated extracolonic cancers.
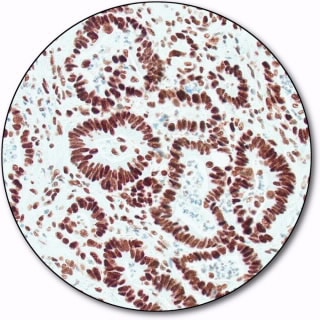
MSH 6
MutS protein homolog 6 (MSH6) is part of the mismatch repair (MMR) pathway which is utilized by normal proliferating cells to repair mutations that may occur during DNA replication. Antibodies to MSH6 are a useful aid for classification of tumors of the gastrointestinal tract, including associated extracolonic cancers.
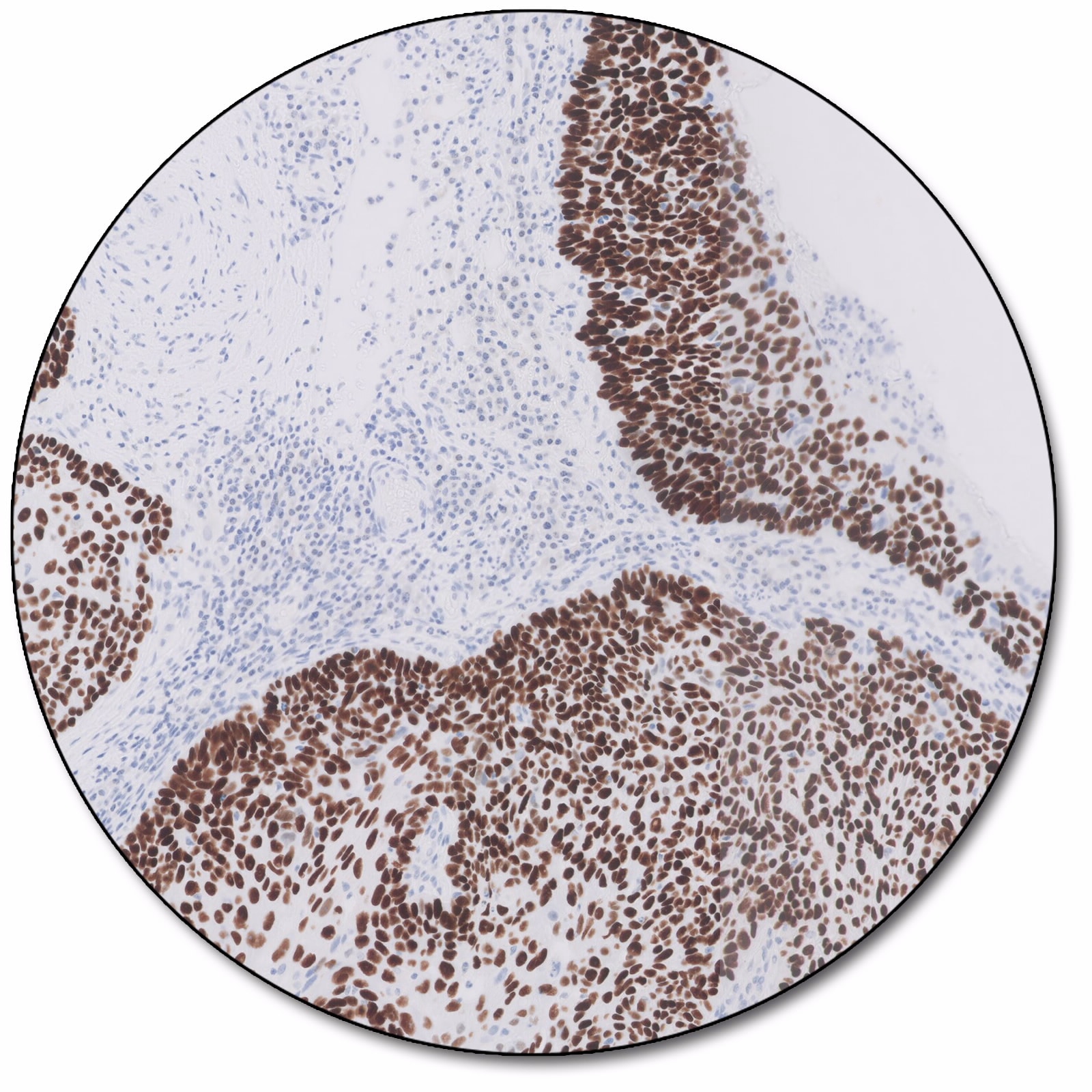
p40
The p63 protein exist in two isoforms TAp63 and ΔNp63. The ΔNp63 isoform is also denoted p40. Antibodies against p63 detect both isoforms whereas p40 antibodies only detect the ΔNp63 isoform.
The p63 protein is regulating cellular growth and its expression is correlated to cellular differentiation. Detection of p40 expression by immunohistochemistry is used as an aid in classification of lung squamous cell carcinoma.
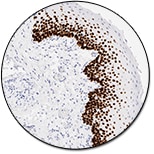
p63 Protein
p63 protein is a member of the p53 tumor suppressor family which also includes the p73 protein. These proteins act as transcription factors that regulate the progression of the cell through its cell cycle and cell death (apoptosis) in response to environmental stimuli, such as DNA damage and hypoxia. The p63 protein is expressed in the nucleus of basal cells in many types of epithelium.
Antibodies to p63 protein may be useful as an aid in the differentiation between benign prostate lesions and prostate adenocarcinoma, between breast carcinoma in situ and breast carcinoma, between squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma of the lung and furthermore to differentiate uterine cervical squamous carcinoma from cervical adenocarcinoma.
Clone DAK-p63 is raised against a synthetic peptide derived from the core DNA-binding domain of human p63 protein thus reacting with TAp63 and ΔNp63 isoforms of p63.
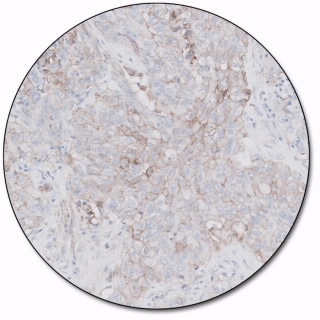
PD-L1
This antibody labels PD-L1 protein in formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue. It is indicated as an aid in the assessment of PD-L1 expression in tumors. The balance between T cell activation, tolerance and immunopathology is regulated by inhibitory signals delivered by programmed death 1 (PD-1) and its ligands, PD-L1 and PD-L2.
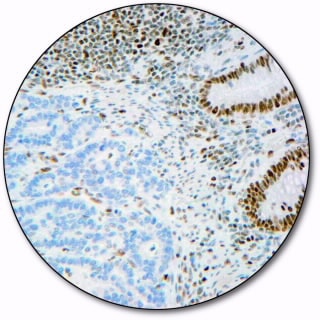
PMS 2
Postmeiotic segregation increased 2 (PMS2) is part of the DNA mismatch repair (MMR) pathway, which is utilized by normal proliferating cells to repair mutations that may occur during DNA replication.
Antibodies to PMS2 may be a useful aid for classification of tumors of the gastrointestinal tract, including HNPCC and associated extracolonic cancers.
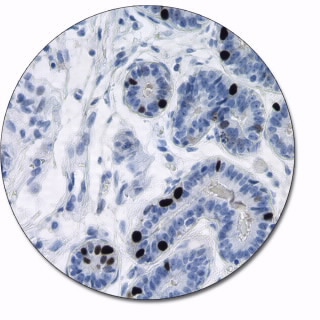
Progesterone Receptor
Progesterone receptor (PR) is a steroid hormone receptor that plays an important role in breast cancer. The absence of PR and estrogen receptor (ER) predicts early recurrence and poor survival of breast cancer patients. The antibody to PR is useful for measuring the relative level of expression of progesterone receptor in breast cancer tissue. This antibody is indicated for assessment of progestrerone receptor status in breast cancer.
